Oral Health Recommendations for People with Hypophosphatasia (HPP)
 Infant Oral Health Issues
Infant Oral Health Issues
It is recommended that all children have a dental “home” by one year of age. Early introduction to the dentist will allow education related to cavity prevention, optimal use of fluoride toothpaste, trauma prevention and education about how to best clean a baby’s teeth.
Early tooth loss that can begin between one and two years of age is not uncommon in children with HPP. The teeth typically fall out on their own and there is no current method to prevent this premature tooth loss.
Children typically need a caregiver to brush their teeth as they will not develop the coordination to do an adequate job until they are about eight years old.
Use a fluoridated toothpaste to clean
your child’s teeth to help prevent tooth decay. (Small smear in children less than three years of age and small pea sized amount for children three years or older).
Children should not be given large amounts of sugar—especially in the form of sweetened beverages, juice or candies.
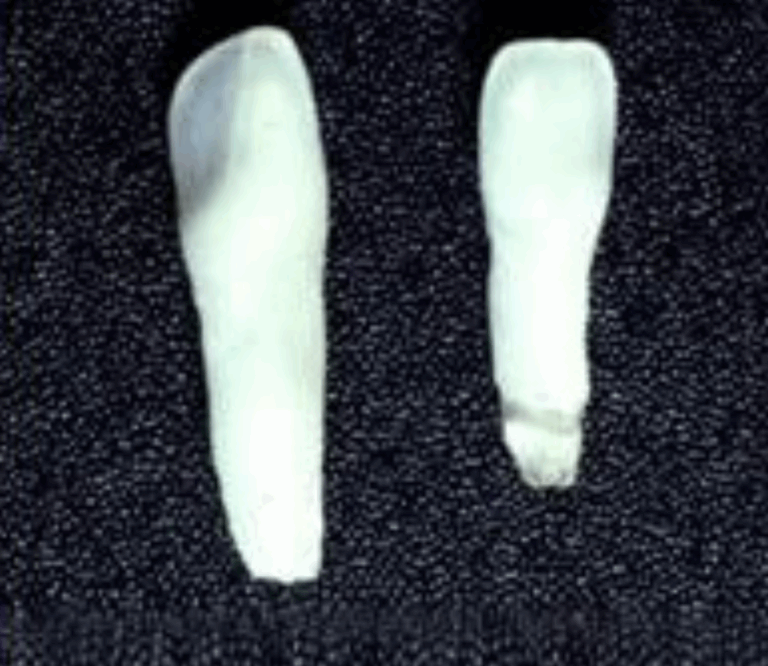
Prematurely Exfoliated primary teeth from an HPP Child
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase that is deficient in people with HPP is important for normal tooth development. This enzyme helps regulate the deposition of minerals like calcium and phosphate during tooth development and abnormal function can result in abnormal formation of the enamel, dentin and root cementum—the three mineralized tissues of a tooth.
Optimal dental care is important for people with HPP to help ensure they do not suffer from dental cavities and to help reduce the risk of tooth loss due to periodontal involvement.
Tooth loss is a commonly observed complication of HPP due to the abnormal development of the cementum layer on the tooth root. Cementum provides the tissue that attaches the tooth to the jaw bone via the periodontal ligament. These
recommendations are offered to help individuals with HPP have the best oral health possible
 Oral Health Care for
Oral Health Care for
Infants and Adolescents
Regular dental visits can help with prevention of cavities through the application of professional strength fluorides and pit and fissure sealants (a plastic coating that fills the grooves and pits of teeth).
If the child has had significant tooth loss in the primary dentition the permanent dentition will likely be at greater risk for having tooth attachment problems.
If orthodontics is indicated there will be increased risk of periodontal problems but some individuals with HPP have been treated successfully with orthodontic therapy.
Mouth guards should be worn for participation in any sport that has the potential of causing dental trauma to help prevent loss of the permanent teeth (e.g. football, baseball, basketball, soccer, etc.)
 Adult Oral Healthcare
Adult Oral Healthcare
Periodontal disease is the loss of the bony support that helps hold the teeth into the jaw. Individuals with HPP are at increased risk for periodontal disease due to the abnormal tooth-bone attachment.
Excellent technique in brushing and flossing as well as regular professional cleaning and health monitoring can help reduce the likelihood of having periodontal disease.
 Tooth Loss Replacement
Tooth Loss Replacement
Tooth replacement may be accomplished through several approaches:
• Fixed Prostheses e.g. crowns and bridges
• Removable Prostheses partial and complete dentures
• Implants surgical screws placed in the bone that support different type of prostheses

